Author: Horvath Csaba

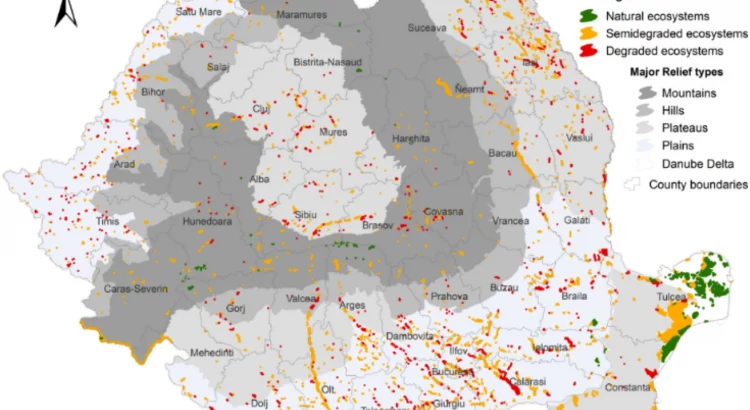
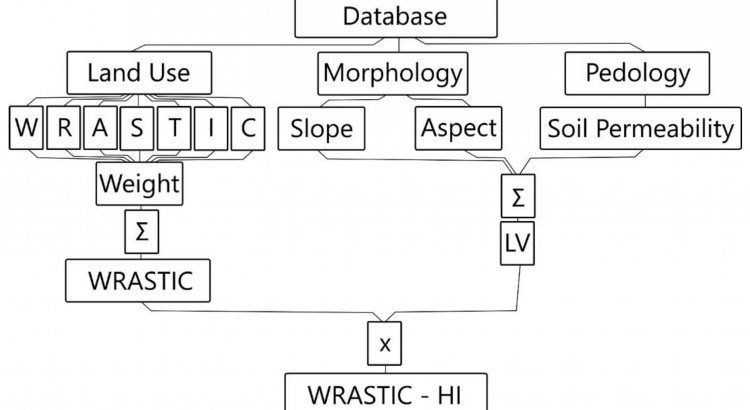
Evaluation of the quality of lentic ecosystems in Romania by a GIS based WRASTIC model
Niculae, Mihaita-Iulian, Avram, Sorin, Corpade, Ana-Maria, Dedu, Silvia, Gheorghe, Carmen Adriana, Pascu, Ionut Silviu, Ontel, Irina, Rodino, Steliana
Scientific Reports volume 11, Article number: 5361 (2021)
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-84802-9
Abstract
Globally, ecosystems are constantly degrading as a result of pressures derived from human activities and climate change. For working towards the restoration of the natural balance, it is necessary to evaluate the deviations induced in the ecosystems, to identify where the changes took place, to know what is their amplitude and to decide where it is possible to get involved. Many aquatic ecosystems are depreciated and their restoration is often difficult. Development of appropriate assessment methodologies will improve the decision-making process in public policies for environmental protection and conservation of biodiversity. This study presents an assessment of the degradation level of lentic ecosystems in Romania, performed through a multi-criteria analysis. An extension of the WRASTIC index (Wastewater-Recreational-Agricultural-Size-Transportations-Indutrial-Cover) was generated, namely WRASTIC-HI. The new index was obtained by including values derived from the Potential Pollutant Load index. The analysis showed that 13% of the evaluated lakes are natural, 56.5% are semi-degraded and 30.5% are degraded. The proposed methodology allows to determine the spatial distribution of the degradation sources and to calculate the corresponding indicators. The results obtained provide a useful tool for diagnostic step that can be used as a cornerstone to further identification of environmental conflicts and proposals for improvement of the ecological status of the lentic ecosystems.
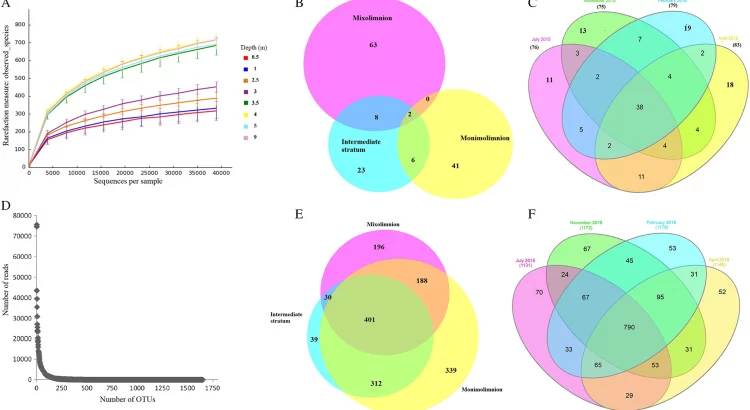
Spatio-temporal insights into microbiology of the freshwater-to-hypersaline, oxic-hypoxic-euxinic waters of Ursu Lake
Andreea Baricz, Cecilia Maria Chiriac, Adrian-Ștefan Andrei, Paul-Adrian Bulzu, Erika Andrea Levei, Oana Cadar, Karina Paula Battes, Mirela Cîmpean, Marin Șenilă, Adorján Cristea, Vasile Muntean, Mircea Alexe, Cristian Coman, Edina Kriszta Szekeres, Cosmin Ionel Sicora, Artur Ionescu, David Blain, William Kenneth O’Neill, Jessica Edwards, John Edward Hallsworth, Horia Leonard Banciu
Environmental Microbiology (2021) 23(7), 3523–3540
https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.14909
Summary
Ursu Lake is located in the Middle Miocene salt deposit of Central Romania. It is stratified, and the water column has three distinct water masses: an upper freshwater-to-moderately saline stratum (0–3 m), an intermediate stratum exhibiting a steep halocline (3–3.5 m), and a lower hypersaline stratum (4 m and below) that is euxinic (i.e. anoxic and sulphidic). Recent studies have characterized the lake’s microbial taxonomy and given rise to intriguing ecological questions. Here, we explore whether the communities are dynamic or stable in relation to taxonomic composition, geochemistry, biophysics, and ecophysiological functions during the annual cycle. We found: (i) seasonally fluctuating, light-dependent communities in the upper layer (≥0.987–0.990 water-activity), a stable but phylogenetically diverse population of heterotrophs in the hypersaline stratum (water activities down to 0.762) and a persistent plate of green sulphur bacteria that connects these two (0.958–0.956 water activity) at 3–3.5 to 4 m; (ii) communities that might be involved in carbon- and sulphur-cycling between and within the lake’s three main water masses; (iii) uncultured lineages including Acetothermia (OP1), Cloacimonetes (WWE1), Marinimicrobia (SAR406), Omnitrophicaeota (OP3), Parcubacteria (OD1) and other Candidate Phyla Radiation bacteria, and SR1 in the hypersaline stratum (likely involved in the anaerobic steps of carbon- and sulphur-cycling); and (iv) that species richness and habitat stability are associated with high redox-potentials. Ursu Lake has a unique and complex ecology, at the same time exhibiting dynamic fluctuations and stability, and can be used as a modern analogue for ancient euxinic water bodies and comparator system for other stratified hypersaline systems.
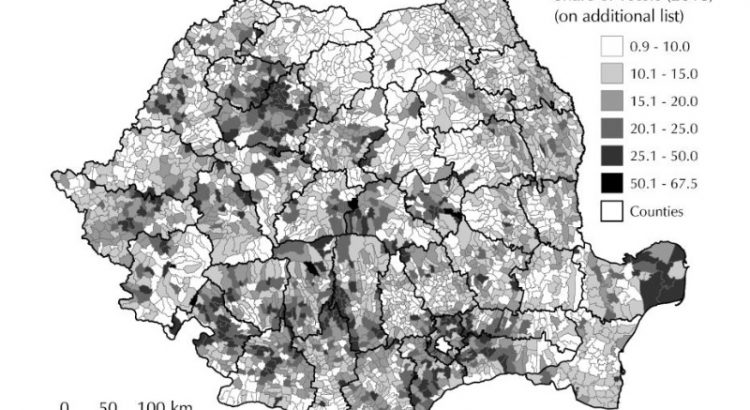
Performing Democracy: An Analysis of Church-Based Electoral Capital in Romania
BÎRSĂNUC ELENA-MANUELA, Cocis Emanuela Adina, GLIGOR VIOREL, MAN TITUS-CRISTIAN, NICULA ALEXANDRU – SABIN, STOICA MIHNEA SIMION
April 2021 Transylvanian Review XXIX(2):291-309 DOI: 10.33993/TR.2020.suppl.2.18
Abstract
Confessional diversity triggers various social and political behaviors of citizens. In terms of the relation between politics and religion, Romania is both a diverse and a complex case study, as the church not only had a strong influence on the historical process of state formation, but still casts a long shadow on political decisions. Therefore, the current study aims to determine a connection between the monastics sites’ location and their influence on the political decisions of citizens, in two national elections that had a major impact on the recent political developments in the country: the 2016 Parliamentary elections and the 2018 Constitutional Referendum (on defining the ‘family’). The confessional and social discrepancies between Romania’s rural and urban areas lead to a comparative analysis of the votes on additional lists for the two events. Results indicate a different degree of clergy implication in the electoral process, depending on the impact of the political event on church reliability. Thus, Romania’s church-based electoral capital is assessed using spatial and statistical analysis, resulting territorial patterns based on voter turnout results.
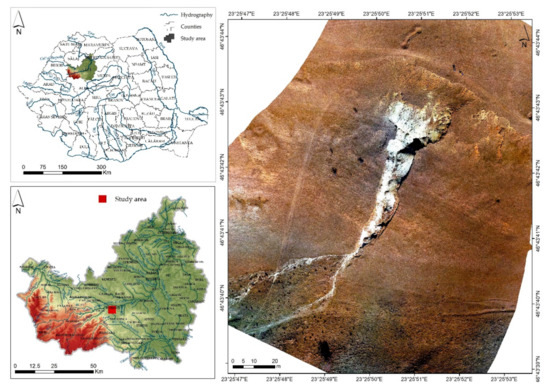
A GIS-Based Spatial Analysis Model Approach for Identification of Optimal Hydrotechnical Solutions for Gully Erosion Stabilization. Case Study
Bilașco, Ș.; Roșca, S.; Vescan, I.; Fodorean, I.; Dohotar, V.; Sestras, P.
Abstract
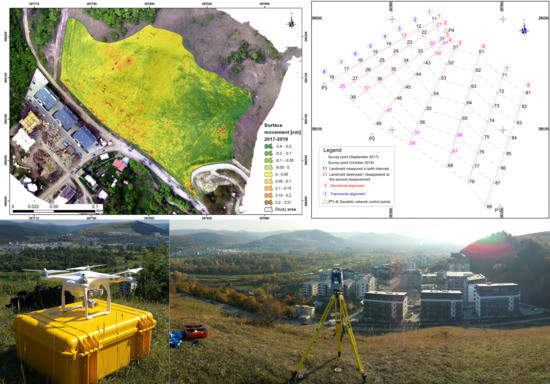
Geodetic and UAV Monitoring in the Sustainable Management of Shallow Landslides and Erosion of a Susceptible Urban Environment
Abstract
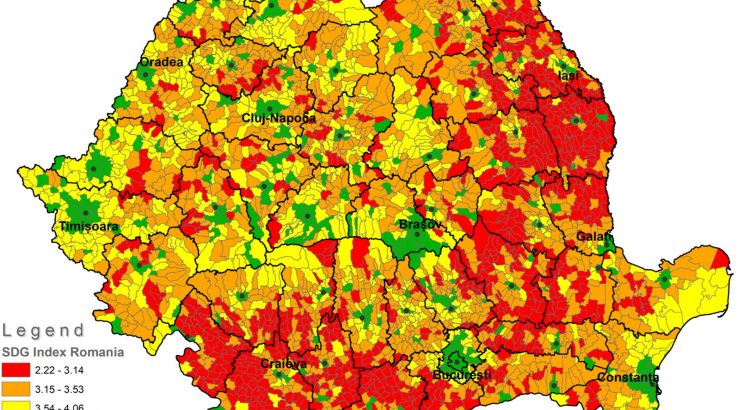
Indicator‐based assessment of local and regional progress toward the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): An integrated approach from Romania
Funding information: Ministry of Research and Innovation CNCS-UEFISCDI, Grant/Award Number: project number PN-III-P4-ID-PCCF-2016-0084, within PNCDI III
Abstract
In order to measure progress in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by 2030, 169 targets have been approved globally. Even though interest in implementing these goals is high, many states have not yet established a set of subnational indicators to measure the implementation of the SDGs and have not completed their own assessment of progress in achieving these global goals. This study aims to measure the progress toward achieving the SDG at local and regional level in Romania by calculating the SDG Index. For the calculation of the SDG Index at subnational level, we propose an integrated approach based on 90 indicators, stored and processed in a PostgreSQL object-relational database. The results show the concentration of the highest performances of sustainable development in some specific geographical areas. The rural areas and the extended peripheral regions in the eastern and southern part of the country are the poorest performers.